According to the Oracle documentation the key features of the Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance are:
- Real-time redo transport
- Secure replication
- Autonomous tape archival
- End-to-end data validation
- Incremental-forever backup strategy
- Space-efficient virtual full backups
- Backup operations offload
- Database-level protection policies
- Database-aware space management
- Cloud-scale architecture
- Unified management and control
- Eliminate Data Loss
- Minimal Impact Backups
- Database Level Recoverability
- Cloud-scale Data Protection
One of the main benefits of introducing the Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance is that it provides the perfect leverage to ensure that all backup and recovery strategies are standardized and optimized in an Oracle best practice manner. In most enterprise deployments you still see that backup and recovery strategies differ over a wide Oracle database deployment landscape.
It is not unseen that backup and recovery strategies involves multiple teams and multiple tools and scripts and that multiple ways of implementation are used over time. By not having an optimized and standardized solution for backup and recovery organizations do not have the ability to have an enterprise wide insight in how well the data is protected against data loss and a uniform way of working for recovery is missing. This introduces the risk that data is lost due to missed backups or due to a non compatible way of restoring.
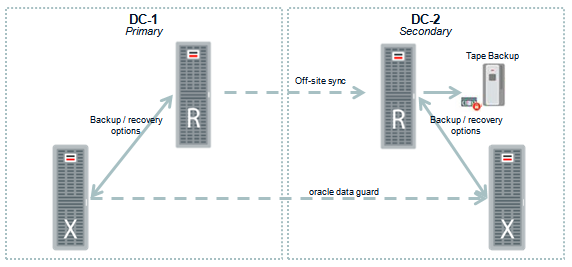
In the below diagram a dual datacenter solution for Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance is shown in which it is connected to a Oracle Exadata machine. However, all databases regardless of the server platform they are deployed on can be connected to the Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance.
When operating a large enterprise wide Oracle landscape customers do use Oracle Enterprise Manager for full end-to-end monitoring and management. One of the additional benefits of the Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance is that it can fully be managed by Oracle Enterprise Manager. This means that the complete management of all components is done via Oracle Enterprise Manager. This in contrast to home grown solutions where customers are in some cases forced to use management tooling for all the different hardware and software components that make the full backup and recovery solution.